When your skin burns, you might be quick to blame the sun's visible light. However, the real culprit is UV radiation — and it’s 100% invisible. Like visible light, UV radiation is a spectrum of frequencies that can be split into distinct bands including UVA and UVB. Each affects the skin differently, and thus requires different protection to keep skin healthy and prevent premature aging.
01
Understanding UV Radiation
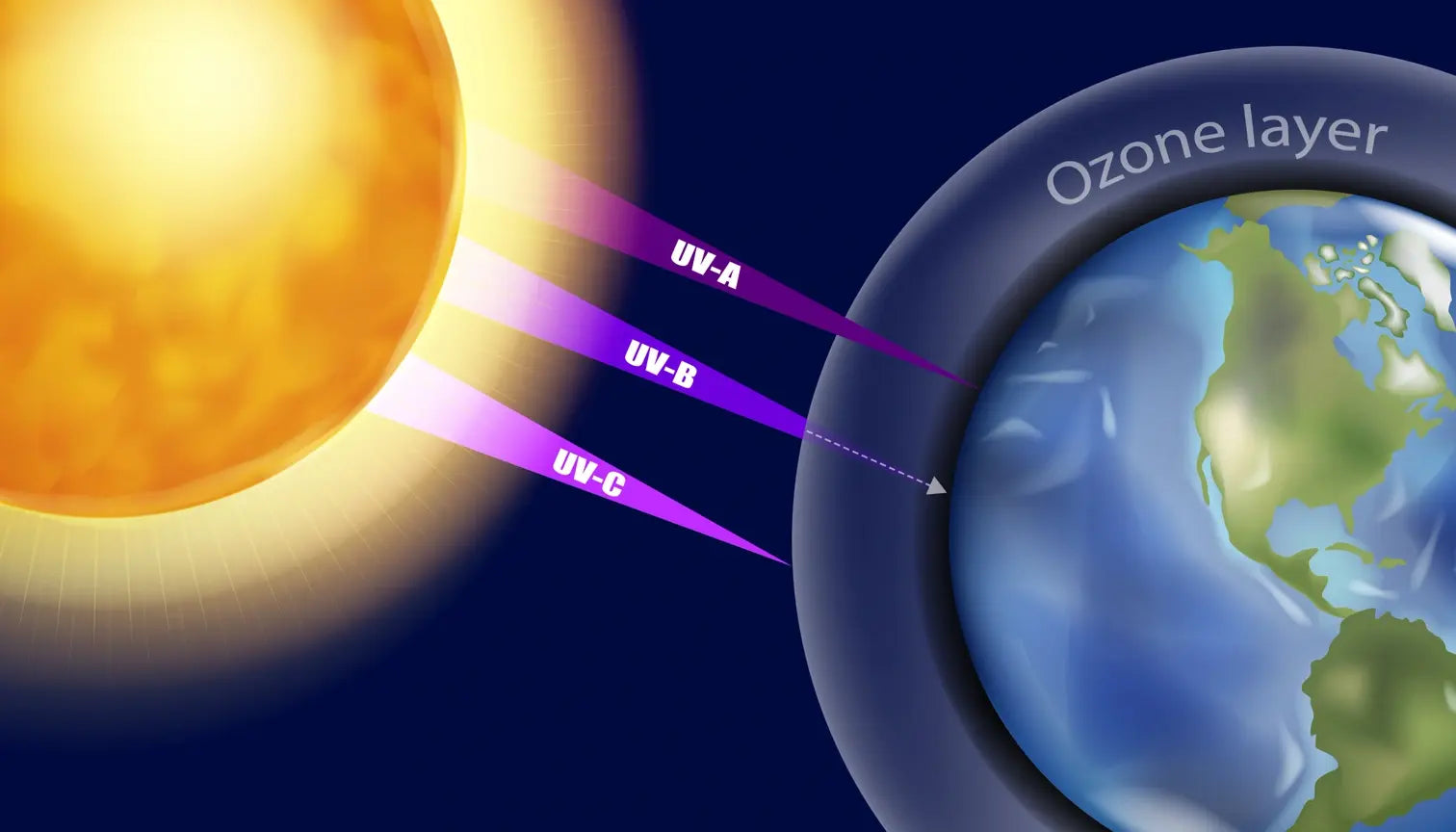
Before diving into the difference between UVA and UVB rays, it's essential to grasp the concept of UV radiation itself and what UV light does to skin. Ultraviolet (UV) radiation is a form of electromagnetic radiation emitted by the sun that causes ionization. When skin cells are exposed to ionization, they experience damage, which weakens the overall health of skin. (1) UV radiation is typically categorized into three types: UVA, UVB, and UVC. Since UVC rays are almost entirely absorbed by the Earth's atmosphere and don’t reach the surface, you only really need to be concerned with UVA and UVB light. (2)

Here’s how UV light impacts the skin: (3)
- It creates free radicals, such as reactive oxygen species (ROS), which damage the proteins, including collagen and elastic fibers, and cause damage to DNA.
- It induces senescence, increasing the number of senescent cells in the skin. Senescent cells secrete a number of harmful biochemicals, including matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) which degrade collagen proteins.
- It degrades skin’s barrier function. When the skin barrier is disrupted, skin’s sensitivity to UV increases, making this a self-perpetuating cycle of cellular damage.
- It destroys the dermal structure, replacing collagen with nonfunctional elastic tissue in the dermis (“solar elastosis”).
- It’s primarily responsible for the photoaged appearance of skin including the five key signs of skin aging: fine lines and wrinkles, enlarged pores, redness, pigmentation, and sagging skin.
02
What is UVB?
UVB rays are short-wavelength (290 - 320 nm), high energy rays; their intensity varies daily, seasonally, and geographically and they can bounce off or be absorbed by the atmosphere. Short-wavelength UVB rays can’t reach very far into the skin and therefore primarily affect the epidermis, the skin's outermost layer. UVB rays are the main culprits behind sunburns and play a significant role in the development of skin cancer. (4)
What are the Impacts of UVB rays?
Because of their shorter wavelength and higher intensity, UVB rays have a more immediate and visible impact on your skin. As these rays penetrate the epidermis, they cause damage to DNA within skin cells and trigger an immune response. This cascade of effects increases blood flow to the affected areas, which causes redness, pain, and inflammation — more commonly known as a sunburn. (4) Prolonged or repeated UVB exposure over time can lead to more severe outcomes, such as the development of skin cancer.
Does My Sunscreen Protect Against UVB Rays?
Look for the Sun Protection Factor (SPF) on your sunscreen. This indicates the level of protection against UVB rays (for both UVA and UVB protection, use a broad-spectrum SPF like our new OS-01 BODY SPF and OS-01 SHIELD — the first sunscreens to prevent and undo UV-induced aging). Interestingly, the incremental increase in protection diminishes as SPF goes up. For instance, the difference in UVB protection between SPF 30 vs SPF 50 is only 1.3%. (5)

Why is this important? Because mineral sunscreens, which are generally considered the safest sunscreen for our bodies and the planet, can become more pasty and produce higher levels of white cast as more of the active ingredient (zinc oxide or titanium dioxide) is added to increase the SPF. As the thickness and white cast increases, you might find that you apply less than the recommended dose in order to blend it in better. Even if you’re using a higher SPF, you could actually be receiving less UVB protection.
03
What is UVA?
UVA rays make up the majority of the UV radiation that reaches the Earth's surface. Because of their longer wavelengths (320 - 400 nm) and lower energy, they’re able to penetrate the atmosphere much easier than other types of UV rays. (6) This means that UVA rays are relatively constant throughout the year, even on cloudy days. These properties also allow UVA rays to penetrate the skin more deeply than UVB rays, affecting the collagen structure of the dermis, the skin's middle layer. (6)

What are the Impacts of UVA Rays?
UVA rays are notorious for their ability to accelerate the skin's aging process. UVA rays penetrate into the dermis, creating reactive oxygen species (ROS), which directly damage collagen fibers. (4) This damage leads to sagging skin, fine lines, and wrinkles. Even though UVA rays are less likely to cause immediate sunburn, don’t underestimate their long-term effects on your skin's health.
04
Does My Sunscreen Protect Against UVA Rays?
As mentioned earlier, looking at your sunscreen’s SPF is only one part of the equation. That’s because SPF only indicates the level of protection against UVB rays. For protection against both kinds of rays, look for these two things:1. Broad Spectrum. This means a sunscreen protects your skin from UVA and UVB rays. Previously, this could have meant any level of UVA protection. However, in 2011, the FDA released new regulations that only allowed sunscreens to be labeled as “Broad Spectrum” if they blocked the absorption of rays within the UVA range. (7) They determine this with a Critical Wavelength Test, in which the UV absorbance of a sunscreen is measured from 290 to 400 nm – the wavelengths that span both UVB (290 - 320 nm) and UVA (320 - 400 nm) – and the area under the curve is calculated. The critical wavelength is the wavelength at which 90% of the curve covers. If this critical wavelength is above 370 nm, then the sunscreen can be considered “broad spectrum” since it absorbs a majority of the rays within the UVA spectrum (320 - 400 nm). In other words, to be “broad spectrum”, at least 90% of the area under the curve must reach 370 nm. (7)

But there’s one problem with the critical wavelength test: It doesn’t tell you how evenly spread the protection is. So, you could have a majority of the absorption happening in the UVB wavelengths and less absorption in the UVA wavelengths, but still pass as a broad spectrum. For instance, both of the sunscreens below would be labeled broad spectrum even though the sunscreen on the right has higher UVA protection.

Cole C., Critical Concepts About Sunscreens. Practical Dermatology Special Section, Clnical Insights. 2, 1-4. 2014.
That’s why the EU and Australia have also issued the following requirement to be labeled as broad spectrum: the UVA protection must be at least 1/3 of the labeled SPF value. (8) This means that if a sunscreen is labeled as broad spectrum in the EU or Australia, the higher the SPF, the higher the UVB and UVA protection. In a study comparing the different broad spectrum regulations, researchers tested 20 sunscreens, and found that 19 would be broad spectrum in the US, but only 11 would be broad spectrum in the EU. (9) 2. PA+ / PPD Scales. Though broad spectrum is helpful, understanding your sunscreen’s UVA protection requires you to sort of read between the lines. That’s why many brands are now directly indicating their UVA protection factor with one of the following two scales. Think of them like the SPF for UVA protection.
- PPD Scale: Commonly used in European countries, PPD (persistent pigment darkening) measures how protective a sunscreen is against a long-term tan caused by UVA. (10)
- PA+ Scale: PA (Protection Grade of UVA) is analogous to PPD, but uses + signs instead of numbers to indicate the level of UVA protection. The PA+ system is used more commonly in Asian countries. (10)

To Summarize:

05
Protect Skin from UVA and UVB Rays with OneSkin
With our new OS-01 BODY SPF and OS-01 SHIELD (FACE SPF), you have all the tools for head to toe protection from UV damage. Both provide broad-spectrum SPF 30+ PA+++ protection with non-nano zinc oxide, potent antioxidants to neutralize free radicals, and our proprietary OS-01 peptide, scientifically proven to reverse skin’s biological age. (11) In fact, they’re the first sunscreens to prevent UV damage and target existing damage at the source with the OS-01 peptide.
Key Takeaways:
- UV radiation, emitted by the sun, causes damage to skin cells. It's divided into UVA, UVB, and UVC rays, with UVA and UVB being of the most concern.
- UVB rays are short-wavelength and primarily affect the skin's outermost layer, the epidermis. They’re responsible for sunburns and play a significant role in the development of skin cancers.
- UVA rays have longer wavelengths and penetrate the skin more deeply, affecting the collagen structure in the dermis. These types of rays are primarily responsible for skin aging.
- To protect skin from UVA and UVB rays, look for a broad-spectrum sunscreen with listed a PPD or PA+ scale to tell you the level of UVA protection.
- New! OS-01 BODY SPF and OS-01 SHIELD offer broad-spectrum SPF 30+ PA+++ protection and are powered by the OS-01 peptide.
References
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3709783/
- https://www.who.int/news-room/questions-and-answers/item/radiation-ultraviolet-(uv)
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/jocd.13007
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8597149/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3460660/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/10907526/
- https://www.jaad.org/article/S0190-9622(12)02042-7/abstract
- https://www.ulprospector.com/knowledge/7288/pcc-eu-spf-regulations-labelling-and-claims/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S019096221730035X
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC3543289/
- https://www.nature.com/articles/s41514-023-00109-1