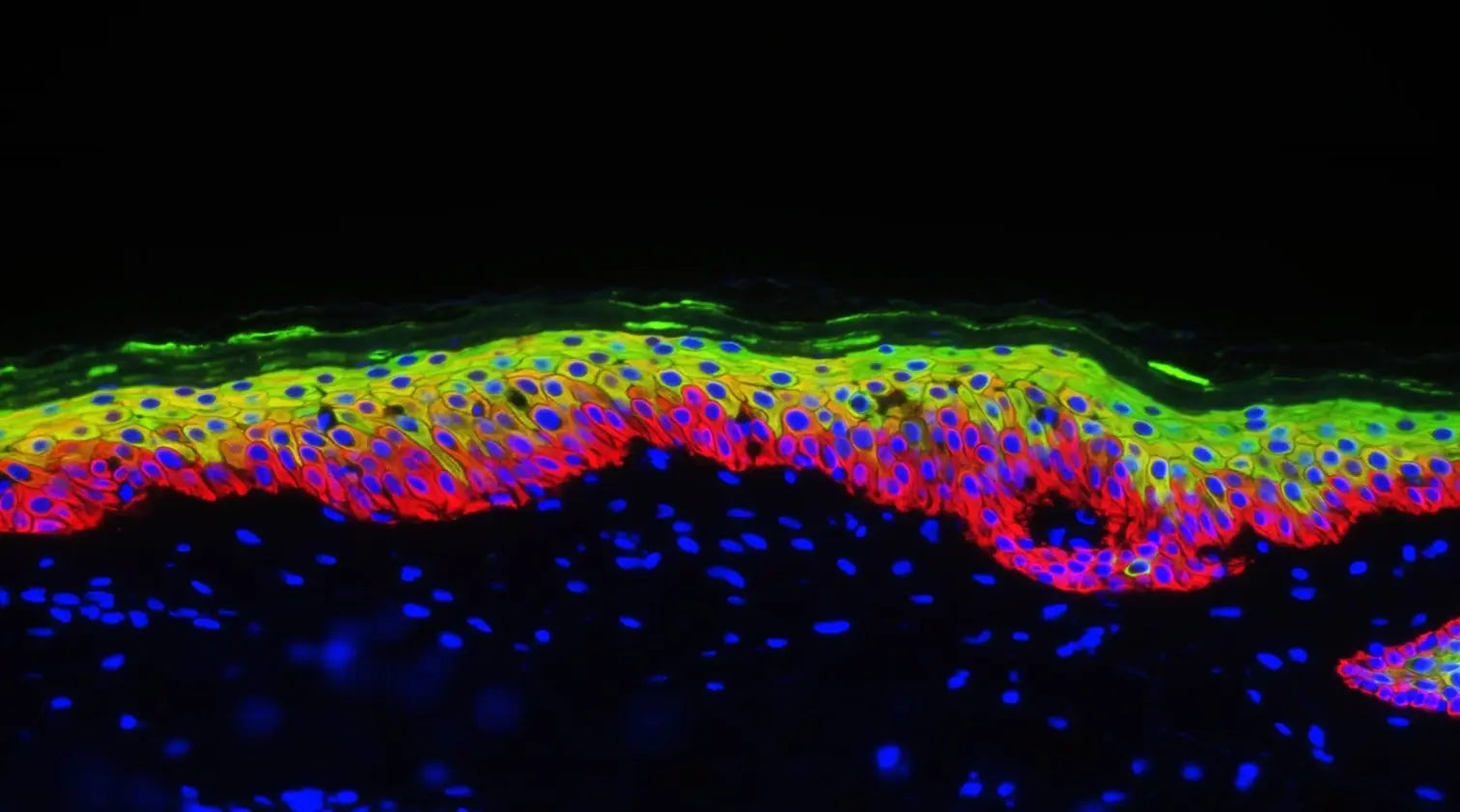
How does young skin function on the molecular level?
- Healthy Collagen & Skin Structure: Youthful skin contains an abundance of collagen, one of the main structural proteins that gives skin its firmness and bounce. Robust collagen production makes skin more resistant to stress and injury. This is partly due to the fact that young skin creates new cells at a higher rate than old skin, replacing damaged cells more quickly.
- A Strong Skin Barrier: As the body’s largest organ, skin plays an essential role in protecting our delicate internal system from outside aggressors. When our skin is young and healthy, it has a strong stratum corneum: the top layer of the epidermis that creates a watertight barrier and works with the immune system to defend against external pathogens.
-
Maintained Homeostatic Function:
Youthful skin is more capable of fulfilling its homeostatic functions, namely water and temperature regulation through sweating and blood flow.1
- Lower Levels of Cellular Senescence: At the heart of all of these factors is the molecular cornerstone of healthy skin: lower levels of cellular senescence. As we age, our skin accumulates senescent cells, dead “zombie cells” that trigger inflammation and induce premature aging in neighboring cells. Skin that acts younger on the molecular level shows lower accumulation of these toxic cells –and therefore lower levels of inflammation, collagen degradation, and barrier dysfunction.
What preventative steps can I take to keep my skin young?
Age-related skin changes start to become visible beginning in our mid-20s with our first fine lines and elasticity changes. This is primarily due to the reduction in collagen production, which will continue to gradually decrease throughout our lives.2 Luckily, some easy lifestyle shifts can make a big difference. It’s never too late to start!
-
Stay Hydrated & Limit Caffeine Consumption
: Studies have shown that dehydration decreases skin elasticity and tautness, while increasing your water consumption can improve thickness of the epidermal and dermal layers.3 If coffee is part of your daily routine, keep your intake moderate. Coffee contains antioxidants, which battle free radicals that contribute to aging.4 However, when consumed in excess, coffee and other caffeinated beverages can dehydrate your skin and compromise the skin barrier. 5
-
Get Plenty of Rest:
The skin goes through most of its repair processes at night–regenerating damaged tissues, replenishing nutrients with increased blood flow, and ramping up collagen production. Studies have shown that people who get at least eight hours of sleep have fewer wrinkles, fewer fine lines, and more moisturized skin.6,7
-
Limit Alcohol & Stop Smoking:
While a single glass of red wine may have its benefits, excessive alcohol consumption has been found to directly impair skin barrier function. Acetone, as one of the main products of alcohol metabolism, has been found to reduce skin thickness and integrity.8 Smoking also reduces the skin’s ability to repair itself; nicotine constricts blood vessels and prevents skin cells from accessing the oxygen and nutrients they need to replicate. This decreases epidermal thickness and causes the skin age faster.9
-
Manage Your Stress Levels:
Hormonal changes that occur when we’re stressed directly impact skin function. Most notably, elevated levels of molecular precursors to cortisol, the key stress hormone, are directly linked to greater inflammation and unhealthy proliferation of skin cells. Plus, higher levels of epinephrine can impair wound healing, which increases the risk of conditions like dermatitis, psoriasis, and acne.10
-
Exercise Regularly:
Research has shown that those extra minutes at the gym may make your skin healthier. One study showed that individuals in their 60s who participated in an aerobic endurance program and engaged in other healthy lifestyle habits had similar dermal thickness to people in their 20s and 30s. This was compared with much thinner dermal layers in sedentary individuals.11
-
Eat More Plants & Less Sugar:
A review published in May 2020 concluded that a diet rich in plants provides the skin with essential nutrients, including vitamins A, C, and E. 12 On the other hand, high-fat diets impair skin barrier function, while consuming too much processed sugar can result in higher rates of inflammation and skin aging.13
Which anti-aging trends should I avoid?
-
Retinol:
While this form of vitamin A has been celebrated for its anti-aging benefits, recent research suggests that retinol may actually accelerate molecular markers of skin aging. 14
- Botulinum Toxin (Botox): Botulinum toxin works via injection by blocking the release of a neurotransmitter from our nerves to our muscles. After treatment, facial muscles are unable to contract, which gradually softens wrinkles. While this effectively makes skin look younger, it does not improve the function of your skin at the molecular level, meaning your skin cells still act like older cells even if your skin looks younger.
-
Chemical Peels:
Chemical peels encourage rapid cell turnover by removing surface skin layers. While peels can result in a thicker epidermis, increased collagen production, and improved hydration, there are risks that cannot be overlooked: infections caused by a weakened of the skin barrier, potential damage to the heart muscle if deep chemicals are used improperly, and irritation that can last for several months depending on your skin type. Stick with at-home exfoliants or find a dermatologist you trust for in-office peels. 15
What type of skincare routine should I use to keep my skin young?
- Wash Your Face: Cleansing your face every night gets rid of sweat, makeup, and toxic pollutants that may have accumulated throughout the day. Plus, a nightly cleanse helps your subsequent skincare steps absorb more effectively. For best results use a cleanser like OneSkin PREP, which has been shown to double the absorption of the OS-01 peptide when used before OS-01 FACE.
-
Exfoliate Regularly:
Removing dead skin build-up has been linked to greater collagen production and improved blood flow. Avoid aggressive scrubs and harsh acids that sting or leave your skin red. A gentle weekly exfoliant with alpha hydroxy acids will keep your skin smooth. 16
-
Use SPF Every Single Day: On the cellular level, sun exposure causes cells to prematurely enter senescence
. UV-induced senescent cells show high expression of MMPs, a family of enzymes that break down collagen.17 When selecting a sunscreen, look for an SPF of 30+ with broad-spectrum protection against both UVA and UVB rays to safeguard against potential sun damage. 18
-
Look for Products with Antioxidants
: Throughout our day and with increasing age, free radicals accumulate on our skin, increasing inflammation and reducing collagen production. Antioxidants like vitamin C help neutralize free radicals before they can do damage.19
Is there anything I can do to reverse damage that’s already occurred?
While prevention is important, recent breakthroughs in longevity science have made it possible to actually reverse damage that’s already been done – helping your skin cells act younger on the molecular level. Enter OS-01: our breakthrough peptide proven to reverse the biological age of skin and maximize skin health at the molecular level. 14
OS-01 has been shown to reduce a key marker of cellular senescence in skin
Cellular senescence is at the heart of all skin aging. By reducing it, we can help skin cells get back to their youthful function. In lab research on ex vivo human skin samples, the OS-01 peptide was shown to reduce CDKN2A, a marker associated with cellular senescence. This indicates that our peptide effectively mitigates the natural elevation of cellular senescence and helps prevent skin aging. 14
The OS-01 peptide reduces senescent cells in skin

SA B-Gal (senescence-associated beta galactosidase) stained image of HGPS HDFs (human dermal fibroblasts from patient-derived samples with Hutchinson-Gilford progeria syndrome) treated with 50uM OS-01 peptide for 2 days compared to untreated control (Zonari, A., et al. npj Aging, 2023).
In this study, our scientists found that exposure to the OS-01 peptide reduced senescent cells (blue) by up to 50% while maintaining the total number of cells. 14 This means that the OS-01 peptide promoted not just the reduction of senescent cells, but also the renewal of healthier ones.
By addressing cellular senescence, OS-01 can help extend the length of time that your skin operates at peak health. The bonus? Smoother lines, brighter tone, and the glow of healthy skin. Ready to see the results yourself? Find OS-01 in our collection of science-backed topical supplements.
- Truly youthful skin doesn’t just look good: at the molecular level, it’s functioning smoothly to keep every essential skin function working at peak performance.
- To help your skin cells maintain their youthful function at a molecular level, you should get enough sleep, eat a balanced diet, exercise, and avoid smoking and excessive drinking.
- Want anti-aging benefits that are more than skin deep? Avoid treatments like retinol, botox, and harsh medical peels. While these may help the skin look younger, they have not been shown to extend skin health at the molecular level.
- Instead, focus on a simple preventative skincare routine: nightly cleansing, regular exfoliation, daily use of SPF and skin care products with antioxidants can prevent age-related damage.
- Want to reverse damage that’s already been done and help your skin cells act younger? Try our OS-01 peptide, which has been shown to reduce the root cause of skin aging at the molecular level.
- Functions of the Integumentary System | Boundless Anatomy and Physiology
- https://www.realsimple.com/beauty-fashion/skincare/anti-aging/aging-skin-concerns#:~:text=According%20to%20the%20doctors%20on,lead%20to%20conditions%20like%20melasma
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2908954/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6276298/
- https://thegoodfaceproject.com/articles/coffee_alcohol_water_skin
- https://www.samhealth.org/about-samaritan/news-search/2019/05/29/importance-of-sleep-to-your-appearance-and-skin/
- https://academic.oup.com/sleep/article/36/9/1355/2453883?searchresult=1
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7146365/#:~:text=In%20general%2C%20the%20effect%20of,stress%20to%20produce%20inflammatory%20damage
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7146365/#:~:text=In%20general%2C%20the%20effect%20of,stress%20to%20produce%20inflammatory%20damage
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4082169/
- https://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2014/04/16/younger-skin-through-exercise/
- Diet and Dermatology: The Role of a Whole-food, Plant-based Diet in Preventing and Reversing Skin Aging-A Review, The Journal of Clinical and Aesthetic Dermatology, May 2020
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7146365/
- Zonari, A., et al. Senotherapeutic peptide treatment reduces biological age and senescence burden in human skin models. Npj Aging, 9(1), 1-15. 2023.
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/tests-procedures/chemical-peel/about/pac-20393473#:~:text=A%20chemical%20peel%20can%20lead,the%20heart%20to%20beat%20irregularly
- https://www.healthline.com/health/how-to-exfoliate#how-to
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022202X20322843#:~:text=UVA%20and%20UVB%20radiation%20induces,to%20UVR%20from%20the%20sun
- https://www.thepioneerwoman.com/beauty/skin-makeup-nails/a36031234/mineral-vs-chemical-sunscreen/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5579659/